Shea Butter Process
Shea Butter is a natural product derived from the nuts of the shea tree, which is native to Ghana. The process of making shea butter involves several steps that ensure the highest quality and purity. Want to learn more about this process? Read on!

Harvesting
The process begins with the collection of the shea nuts. The fruits are collected from the shea tree by women in rural communities. The nuts are picked from the ground after they naturally fall from the tree.
Home processing
Before the shea nuts are sent to the processing facility, women in the community handle the initial stages at home. This includes depulping the shea fruit, par-boiling and sun-drying nuts. Once dried, the nuts are cracked open to get the kernels, which are then sorted (the bad ones are discarded). After this, the nuts are sun-dried and stored in jute bags and placed on pallets, ready for next steps in the processing chain.


Boiling and drying
The cleaned nuts are boiled to soften the shells and make them easier to crack. After boiling they are spread out in the sun to dry, with any bad nuts removed during this stage. This step helps in preserving the nuts and making the next process more efficient.
Cracking and roasting
The dried nuts are then cracked to remove the hard shells and extract the kernels inside. These kernels are roasted over a fire to enhance their natural oils.
Traditionally, cracking is done by hand using stones, while more modern, machines are used for cracking and roasting. This reduces the physical strain significantly.


Grinding and Milling
The roasted nuts are ground into a thick, dark brown paste. Traditionally, this is done using stone grinders or pestles, a method that requires considerable time and effort. In our production site, mechanical mills are used to grind the nuts quickly and efficiently, allowing for larger quantities to be processed in a shorter time.
Kneading
The paste is then mixed with water and kneaded thoroughly to seperate fats from other components. This process helps in forming a creamy, butter-like consistency.
Traditionally, this process is done by hand. Women spend hours kneading the paste to achieve the right texture. At our production facility, machines are used to knead the paste much more efficiently.
The waste from the paste, known as "cake", is used to fuel the fire for roasting, creating a sustainable cycle.

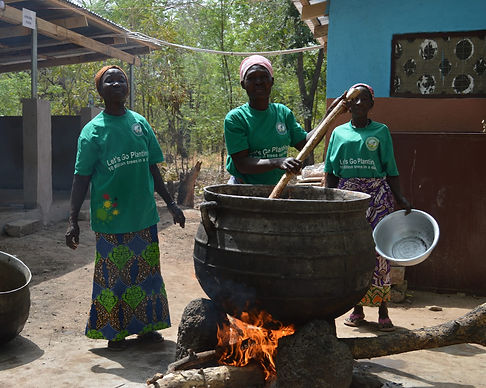
Boiling and Purification
The kneaded paste is boiled to separate the pure shea butter from impurities. During this process, the butter rises to the surface, while the unwanted residues settle at the bottom.
Cooling and solidification
Once the pure shea butter is extracted, it is left to cool and solidify. The final product has a smooth, creamy texture and is ready for packaging and use.
Shea butter is distributed worldwide for use in skincare, haircare and culinary applications.

